In the evolving landscape of medical education, the need for precise, competency-based training is more critical than ever. Residency and fellowship programs across various specialties face the challenge of ensuring that their trainees meet the stringent competencies set forth by major accreditation bodies. Xuron’s innovative AI-powered Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) platform addresses these needs by providing realistic, targeted simulations that aim to close specific non-technical skill gaps identified by these programs.

Identifying the Gaps
Despite the rigorous training provided by residency programs, several gaps persist in the current system across various specialties:
- Competency Deficiencies: For example, up to 9.1% of Family Medicine residents can be classified as residents in difficulty, failing to meet the required level of competence in one or more of the ACGME core competencies.1
- Professionalism And Interpersonal Skills Issues: Both surgical and non-surgical specialties have issues with professionalism and interpersonal skills being the most common reason for remediation.1,3,4,5
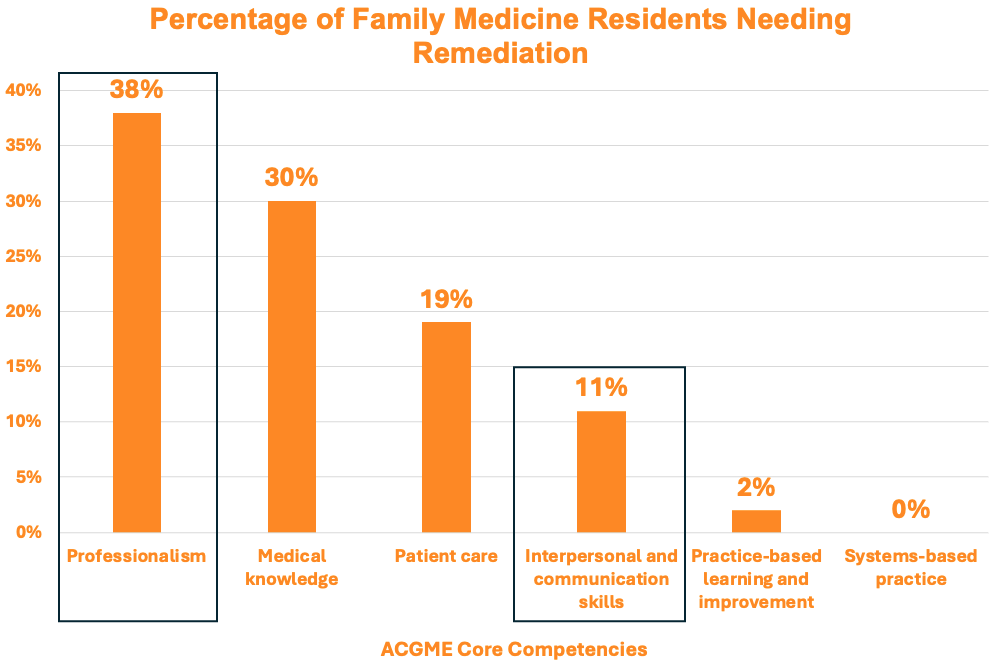
Reference: Frazier W, Wilson SA, D’Amico F, Bergus GR. Resident Remediation in Family Medicine Residency Programs: A CERA Survey of Program Directors. Fam Med. 2021;53(9):773-778.
- Early Identification: In Family Medicine, most residents (86%) requiring remediation are identified before completing their first year of residency.3
- Resource-Intensive Remediation: The remediation process for these residents is taxing on both resident and faculty resources, requiring considerable time and effort in the form of increased supervision, communication needs, and duplication of patient care.
These gaps, although highlighted in Family Medicine and Urology, are present in other specialties as well, emphasizing the need for more comprehensive, effective, and scalable training solutions.2

Closing the Gaps with Xuron
Alignment with Accreditation Competencies
- Competency-Based Training: Xuron’s simulations are meticulously crafted to align with the competencies and milestones required by major accreditation bodies, such as ACGME.
- Targeted Skill Development: The platform focuses on critical skills identified by residency programs, ensuring that residents meet and exceed the required competencies.
Personalized and Adaptive Learning
- Tailored Simulations: Each simulation is powered by AI, allowing it to adjust to the individual learner’s level and progress, ensuring training that is both challenging and appropriate.
- Real-World Scenarios: Virtual simulations mirror real-life clinical scenarios, providing residents with realistic practice opportunities.
- Unlimited Practice: Learners can practice as many times as they want, anytime and anywhere.
Instant Feedback and Continuous Improvement
- AI-Generated Feedback: The platform provides instant, detailed feedback, highlighting areas of strength and pinpointing specific competencies needing improvement.
- Continuous Learning Loop: This feedback loop is essential for helping trainees achieve proficiency in critical skills such as clinical decision-making, patient communication, and empathetic patient care.

Conclusion
By integrating technology like Xuron’s AI OSCE platform, medical education can effectively address the identified gaps, reducing the resource-intensive nature of the remediation process. This ensures that residents, fellows, and medical students are well-equipped to meet the demands of their respective fields, ultimately enhancing the quality of healthcare training.

Written By:
DR. BORIS ROZENFELD
Dr. Boris Rozenfeld is a vanguard in medical education, melding his extensive clinical knowledge with a flair for innovative learning design. At the helm of transformation initiatives in healthcare education, His significant contributions include revolutionizing the American Heart Association’s certification programs with adaptive learning technology, significantly boosting knowledge acquisition and practitioner proficiency.
With a career spanning over nine years in continuing medical education (CME), Boris has a rich history with esteemed organizations such as Pri-Med and RMEI, where he created impactful educational programs for both generalists and specialist clinicians. A fervent proponent of generative AI, Boris is at the cutting edge, continuously exploring and implementing new educational designs that integrate large language models.
His dedication to the future of healthcare education is unwavering. Boris is committed to developing sustainable and scalable training solutions that seamlessly marry clinical excellence with contemporary educational strategies.
References
- Reamy BV, Harman JH. Residents in trouble: an in-depth assessment of the 25-year experience of a single family medicine residency. Fam Med. 2006;38(4):252-257.
- Katz ED, Dahms R, Sadosty AT, Stahmer SA, Goyal D; CORD-EM Remediation Task Force. Guiding principles for resident remediation: recommendations of the CORD remediation task force. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(suppl 2):S95-S103.
- Frazier W, Wilson SA, D’Amico F, Bergus GR. Resident Remediation in Family Medicine Residency Programs: A CERA Survey of Program Directors. Fam Med. 2021;53(9):773-778.
- Svystun O, Ross S. Difficulties in residency: an examination of clinical rotations and competencies where family medicine residents most often struggle. Fam Med. 2018;50(8):613-616.
- Han DS, Badalato GM, Murano TE, Anderson CB. Resident Remediation: A National Survey of Urology Program Directors. J Surg Educ. 2024 Apr;81(4):465-473. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2023.12.011. Epub 2024 Feb 21. PMID: 38383239.