Embodied AI agents are artificial intelligence (AI) systems designed to interact with their environment and users in a physical or virtual form that mimics human presence. These agents exhibit human-like behaviors, engage in conversations, and perform tasks in a way that appears natural and intuitive.
Key Characteristics of Embodied AI Agents
- Physical or Virtual Presence: These agents exist in physical forms like robots or virtual forms like avatars in VR environments, allowing direct and intuitive interaction.
- Human-like Interaction: Embodied AI agents exhibit behaviors and communication styles similar to humans, including verbal communication, body language, facial expressions, and gestures, creating natural interactions.
- Interactivity: These agents engage in real-time interactions, responding to inputs and adapting their behavior based on context and user actions.
- Context Awareness: They understand and interpret the context of their environment and interactions, providing relevant and appropriate responses and actions.
- Learning and Adaptation: Embodied AI agents incorporate machine learning algorithms that enable them to learn from interactions and improve their performance over time, adapting to new situations and users to provide personalized experiences.
Interaction Types with AI Agents
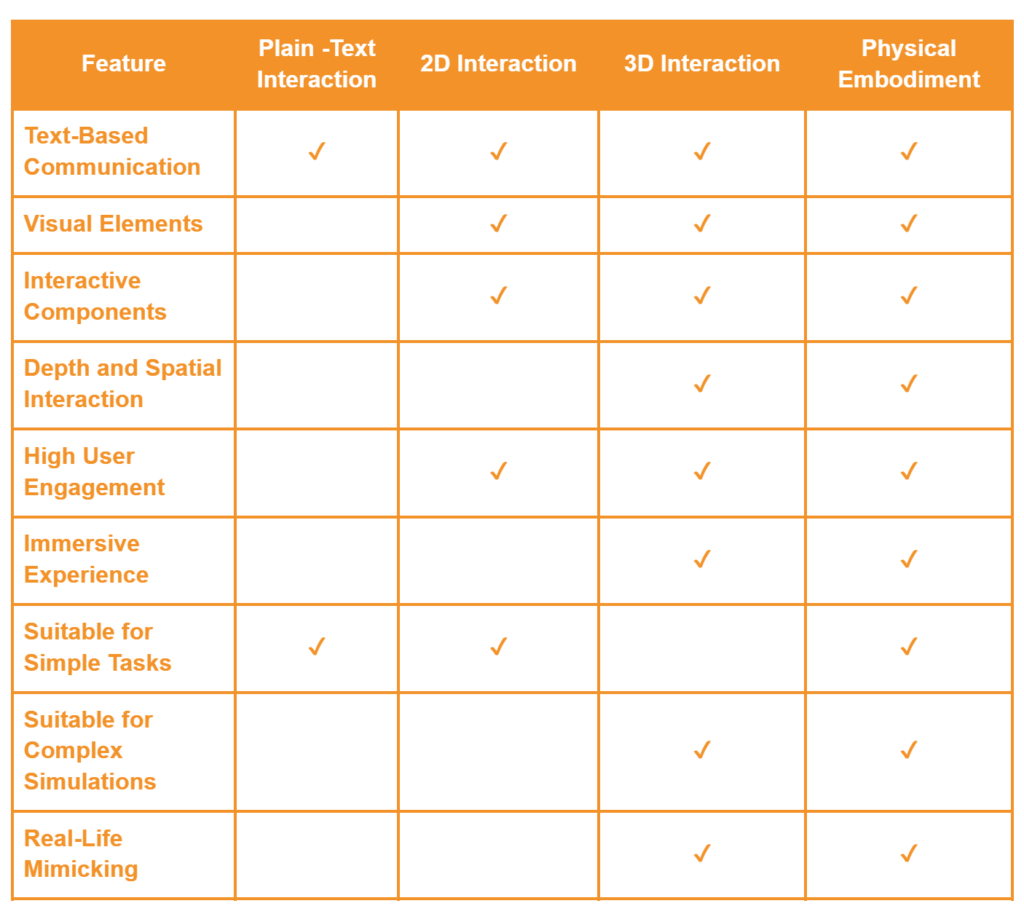
Plain Text Interaction
Plain text interaction involves communication with AI agents through written text on a screen. Users input text, and the AI agent responds with text. This form is straightforward, accessible, and widely used in customer service and basic conversational agents.
Two-Dimensional Interaction
Two-dimensional (2D) interaction includes graphical elements such as text, images, and buttons on a flat screen. It provides a richer user experience compared to plain text by offering visual cues and interactive components. Examples include mobile apps and web interfaces where users click, drag, and interact with different elements.
THREE-DIMENSIONAL INTERACTION
Three-dimensional (3D) interaction involves depth and spatial interaction, common in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) environments. Users interact with AI agents as 3D avatars, moving and gesturing in a simulated space. This immersive method is effective for training, education, and therapeutic applications. While VR/AR hardware can be cost prohibitive, an alternative is 3D interaction on a flat screen (mobile, tablets, desktop).
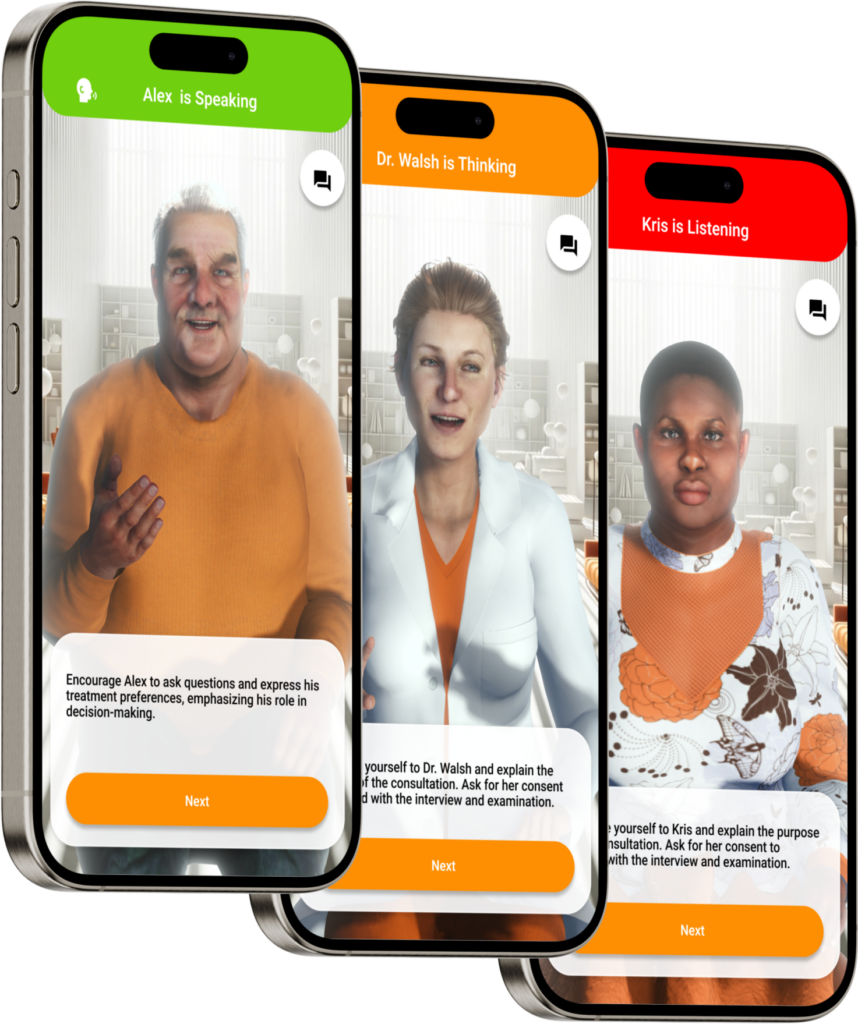
PHYSICAL EMBODIMENT
Physical AI agents, or robots, combine AI with physical bodies to do real-world tasks. They use sensors, make decisions, and perform actions, making work more efficient and providing a hands-on AI experience. In healthcare, for example, robots help with surgeries and keep elderly people company. In industry, they automate manufacturing processes. With advanced technology in machine learning and robotics, these robots can move through complex environments and interact safely with humans, making AI more useful and impactful in everyday life.
Use of Embodied Agents in Healthcare and Medical Education

Embodied AI agents are revolutionizing healthcare education by providing interactive, realistic training environments. These agents are used across various disciplines, enhancing learning experiences through simulation and immersive technologies.
Benefits in Healthcare Training
- Realistic Simulations: They provide lifelike simulations of patient interactions, allowing users to practice clinical skills and decision-making in a safe environment.
- Immediate Feedback: AI agents can give instant feedback on clinical decisions, helping learners to improve their skills more rapidly.
- Accessibility: These simulations are accessible anytime and anywhere, enabling continuous learning without the constraints of physical patient availability.
- Skill Practice: Embodied agents allow users to practice essential skills such as patient communication, wound care, and emergency response in a controlled setting.
- Emotional Preparedness: They help users prepare for emotionally challenging situations by simulating interactions with distressed or difficult patients.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: These agents facilitate interdisciplinary training, where different healthcare providers can practice working together, enhancing teamwork and communication.
- Consistency in Training: Embodied agents ensure consistent training experiences for all users, reducing variability and enhancing the standardization of medical education.
- Personalized Learning: AI can adapt the training scenarios to match the learner’s progress and needs, providing a tailored educational experience.
Potential Obstacles
- Technical Limitations: The effectiveness of embodied agents depends on the sophistication of the technology, which can sometimes be limited by current advancements and resources.
- User Acceptance: There may be resistance from learners and educators who are accustomed to traditional training methods. Ensuring user acceptance and proper training on how to use these technologies is crucial.
- Cost: Implementing advanced AI and VR systems can be expensive. Institutions need to consider the cost-benefit ratio and ensure sustainable investments.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in healthcare education raises ethical questions regarding data privacy, the accuracy of simulations, and the potential replacement of human educators.
Near-Term Future of Embodied Agents
In the next 1-2 years, multimodal technology will become widespread, enabling embodied agents to see and hear users. These advanced agents will analyze emotions, tone, and other audio cues to provide personalized and effective feedback. Eventually, they will also interpret body language, allowing for more tailored and actionable responses.
Beyond multimodal models, general-purpose robotics models are emerging. These robots use data from teleoperation and simulation, leveraging natural language to perform complex real-world tasks in dynamic environments. They take in visual data, sensor data on joint positions and touch, and output motor control to the robot, providing a richer set of control systems. This evolution will create highly customized learning experiences, focusing on specific skills at a granular level, significantly improving education and training quality.

Conclusion
Embodied AI agents offer transformative benefits in healthcare education and training. They provide realistic, accessible, and consistent training environments that enhance clinical skills and emotional preparedness. However, it is essential to address technical, acceptance, cost, and ethical challenges to maximize their potential and ensure effective implementation.

Written By:
DR. BORIS ROZENFELD
Dr. Boris Rozenfeld is a vanguard in medical education, melding his extensive clinical knowledge with a flair for innovative learning design. At the helm of transformation initiatives in healthcare education, His significant contributions include revolutionizing the American Heart Association’s certification programs with adaptive learning technology, significantly boosting knowledge acquisition and practitioner proficiency.
With a career spanning over nine years in continuing medical education (CME), Boris has a rich history with esteemed organizations such as Pri-Med and RMEI, where he created impactful educational programs for both generalists and specialist clinicians. A fervent proponent of generative AI, Boris is at the cutting edge, continuously exploring and implementing new educational designs that integrate large language models.
His dedication to the future of healthcare education is unwavering. Boris is committed to developing sustainable and scalable training solutions that seamlessly marry clinical excellence with contemporary educational strategies.
Further Reading
- Morrow E, Zidaru T, Ross F, Mason C, Patel KD, Ream M, Stockley R. Artificial intelligence technologies and compassion in healthcare: A systematic scoping review. Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 17;13:971044. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.971044. PMID: 36733854; PMCID: PMC9887144.
- Mergen M, Junga A, Risse B, Valkov D, Graf N, Marschall B; medical tr.AI.ning consortium. Immersive training of clinical decision making with AI driven virtual patients – a new VR platform called medical tr.AI.ning. GMS J Med Educ. 2023 Apr 17;40(2):Doc18. doi: 10.3205/zma001600. PMID: 37361242; PMCID: PMC10285366.
- Sonlu, Sinan, et al. “The Effects of Embodiment and Personality Expression on Learning in LLM-based Educational Agents.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.10993 (2024).

